
Pixel Biosciences(Suzhou) Co., Ltd. has made progress in long-chain RNA synthesis, and successfully achieved the enzymatic synthesis of 200nt RNA.
We are thrilled to announce that Pixel Biosciences(Suzhou) Co., Ltd. has made another significant advancement in RNA synthesis. Leveraging our nMECA technology platform, we have successfully achieved the enzymatic synthesis of 200nt RNA.
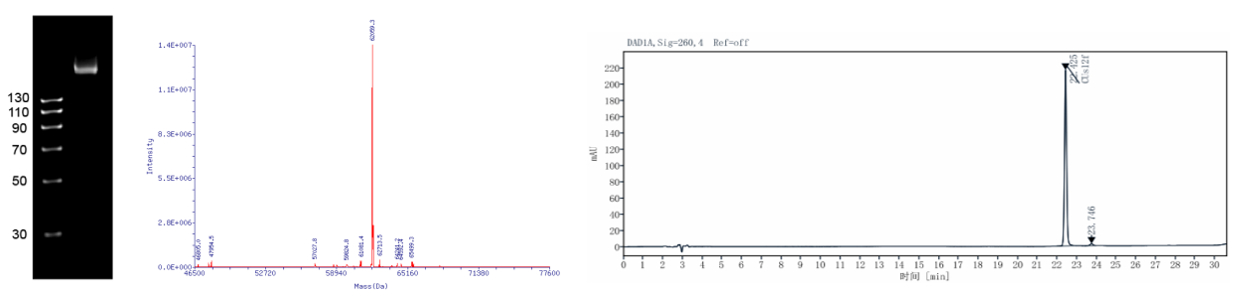
Figure 1: RNA Quality Control Results
Left: Urea-PAGE Electrophoresis; Center: LC-MS Spectrometry; Right: HPLC Analysis
Our products maintain high quality, as shown in Figure 1. Urea-PAGE electrophoresis demonstrates a single, target-sized band consistent with theoretical predictions. HPLC analysis indicates a purity of over 90%, measured using the peak area normalization method. LC-MS confirms the molecular weight with a deviation of less than 0.05% from the predicted value.
Our progress in long-chain RNA synthesis significantly supports the development of prime editing technology.
Prime editing is an emerging gene-editing technique that allows for the precise conversion of all four bases without needing an additional DNA template. It can also efficiently perform multi-base insertions and deletions, inserting up to 44bp and deleting up to 80bp[1]. This system combines the advantages of CRISPR/Cas9 and base editing systems, offering superior benefits. Unlike traditional HDR methods, prime editing does not require DNA double-strand breaks, enhancing its safety.
In prime editing, the length of pegRNA often exceeds 100 nt. As this technology advances, the required RNA lengths continue to increase. Our recent breakthrough in RNA synthesis length fully meets the demands of RNA lengths used in prime editing.
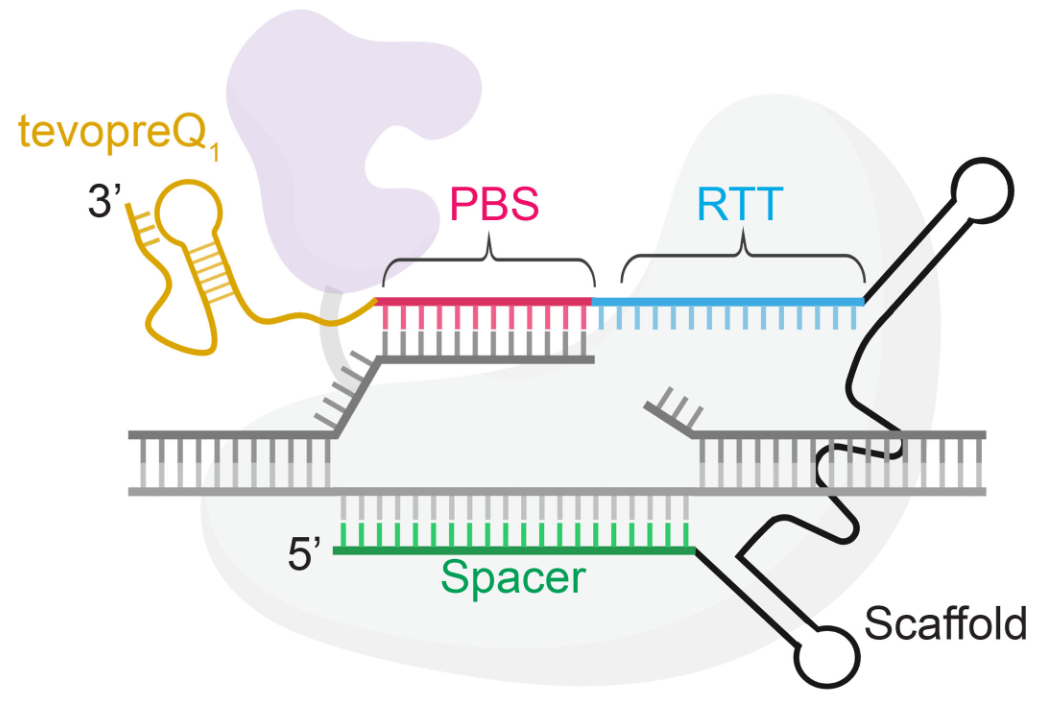
Figure 2: Schematic of epegRNA Structure (Length: 158nt)[2]
Our company will continue to focus on the research and optimization of RNA enzymatic synthesis technology, aiming to further enhance synthesis length and purity. Additionally, we look forward to collaborating with more research institutions and enterprises to advance RNA synthesis technology and its applications, contributing to the progress of life sciences.
[1] Anzalone AV, Randolph PB, Davis JR, Sousa AA, Koblan LW, Levy JM, Chen PJ, Wilson C, Newby GA, Raguram A, Liu DR. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature. 2019 Dec; 576(7785): 149-157. [2] Doman JL, Sousa AA, Randolph PB, Chen PJ, Liu DR. Designing and executing prime editing experiments in mammalian cells. Nat Protoc. 2022 Nov; 17(11): 2431-2468.

