
RNA longmer synthesis has always been a key research focus for PixelBiosciences GmbH. Recently, our R&D team achieved a significant breakthrough in mRNA synthesis using our proprietary nMECA technology platform (an enzyme-splicing-based technique). Compared to traditional in vitro transcription (IVT) technology, nMECA technology dramatically reduces the production of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) byproducts during mRNA synthesis, a remarkable achievement.
As shown in Figure 1, mRNA synthesized using nMECA technology exhibits nearly 100 times less dsRNA content than IVT mRNA. Using RNase-free H2O as a negative control, the dsRNA content in nMECA mRNA showed no significant difference from the control group, indicating that nMECA technology has virtually reached the theoretical limit in controlling dsRNA impurities.
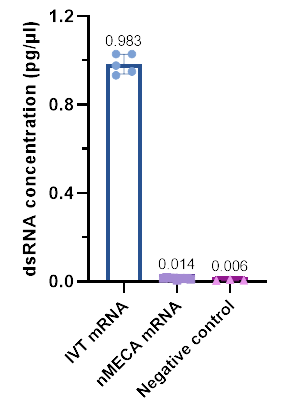
Figure 1: Comparison of dsRNA content between IVT mRNA and nMECA mRNA
In IVT-based mRNA production, dsRNA is one of the most significant contaminants. This transcriptional byproduct not only significantly reduces mRNA transfection efficiency and protein expression levels but also triggers severe inflammatory responses and immune stress. Thus, reducing dsRNA production is a critical step in enhancing the safety and efficacy of mRNA therapeutics.
Current mainstream approaches typically involve optimizing T7 RNA polymerase or improving purification processes to control dsRNA levels. However, these methods are technically complex, require advanced equipment, and cannot completely eliminate dsRNA residues. In contrast, PixelBiosciences' nMECA technology fundamentally reduces dsRNA formation at the synthesis level, paving the way for new possibilities in advancing mRNA therapeutics.
We warmly welcome our peers to explore the potential of nMECA technology in long chain RNA synthesis. If you are interested in our research or technology, please contact us via email at order@pixelbiosciences.com. We look forward to collaborating with you to drive progress in mRNA therapeutics.

